Related
Table of content
The Paths to cluster node converts input paths into interconnected clusters, turning points to Vtx and path segments to Edges. It offers the same advanced options Fuse Clusters does, but takes paths as input!

Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Closed loop | |
| Scope | The scope/selection of input data that are to be processed as closed paths or not. - All processes all input as selected below.- All but tagged inverts the scope based on tags.Default is, all paths are considered open, unless they are tagged with ClosedLoop.
|
| Closed Loop | Whether to consider input data that are part of the scope as closed loop or not. |
| Comma Separated Tags | Tags to check for. Any match uses the inverse of the above value. |
| Fuse Paths | If enabled, emulates the behavior of |
The Path to Clusters node has a very specific order of operation:
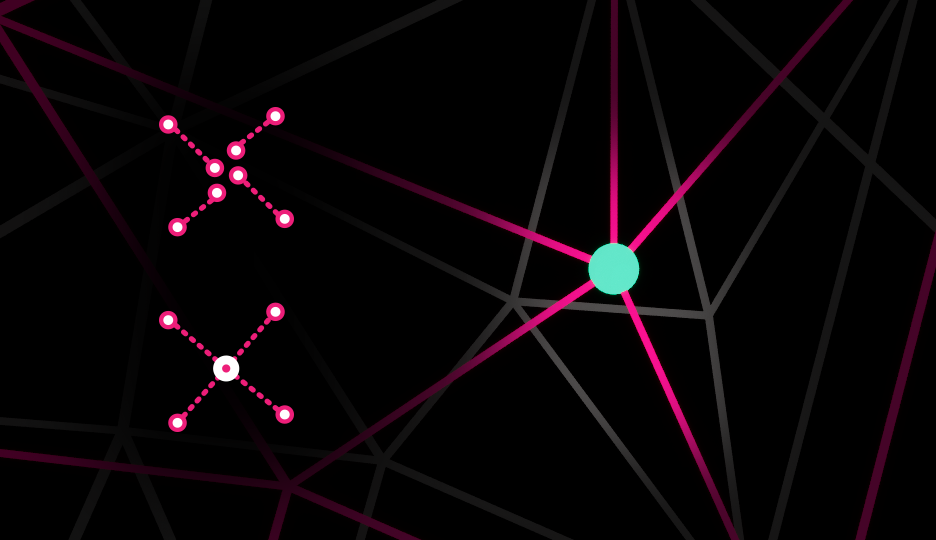
- First collocated points are merged together (Point/Point), turned into
Vtx, andEdgesare created from what was previously path segments.- Points that are merged go through a first blending pass.
- Next, if enabled, any
Vtxthat lie on a foreignEdgewill split that edge into two.A second blending pass is applied
- Last,
Edgesare tested against each other, possibly creating newVtx&Edgesin the process.- A third and last blending pass is applied, where each edges’ endpoints are blended into their resulting intersection point.
While counter intuitive, it is much cheaper to leave
self-intersectionenabled.
Point/Point Settings
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuse Details | |
| Target Distance | Target Distance reference.. Whether to consider point bounds, and if so, how. |
| Fuse Method | Lets you choose the method for finding neighbors & collocated points |
| Voxel Grid Offset | Offset the voxelized grid by an constant amount. By default the center of the grid is 0,0,0, which may look like an undersirable offset. That offset can be manually compensated using this parameter. |
| Inline Insertion |
Using the Octree fuse method is not deterministic by default. Enabling inlined insertion will make it so, at the cost of speed. |
| Source Distance | Source Distance reference. Whether to consider point bounds, and if so, how. |
| Tolerance | |
| Component Wise Tolerance | If enabled, lets you set individual tolerance in world space for each X, Y and Z axis. |
| Tolerance | Uniform tolerance. This represent the radius within which elements will be considered in fuse range. |
| Tolerances | If enabled, represent individual axis’ radius within which elements will be considered in fuse range. |
| Local Tolerance | If enabled, lets your use per-point tolerance value. NOT IMPLEMENTED |
| Outputs | |
Compounded Attribute Namebool
| If enabled, writes a bool flag. true if the point is the result of a merge, false if it’s the “original” one. |
Compound Size Attribute Nameint32
| If enabled, writes the numbers of points that have been compounded/merged into it. |
Point/Edge Intersections
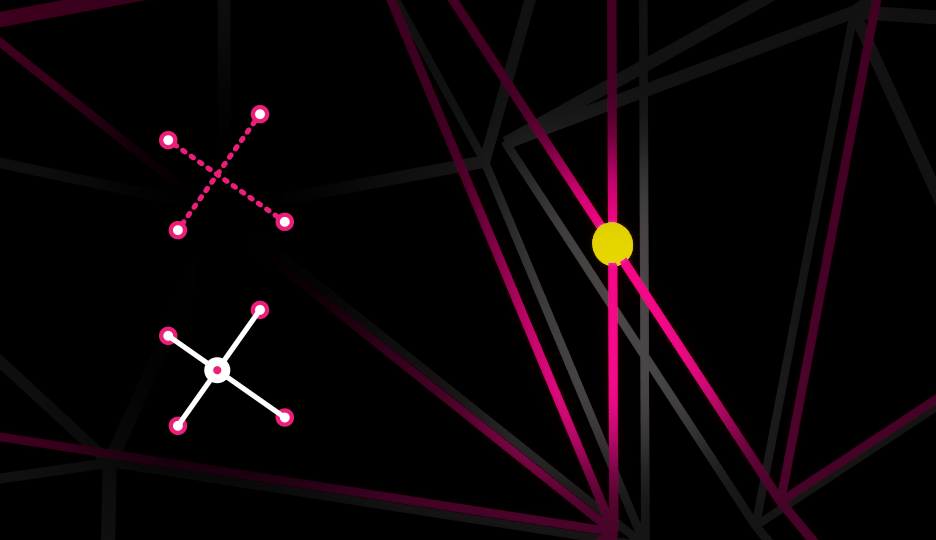
Point/Edge intersections search for Vtx that are lying on Edges they’re not connected to, and if such situation is found, the matching edge is split into new edges as to insert the Vtx there.
The original Edge is removed and the Vtx then becomes connected to the old Edge’ endpoints through 2 new Edges.
| Find Point Edge Intersections | If enabled, fusing will search for point/edge intersections. |

| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Self Intersection | If enabled, a cluster will test if intersection exists against itself. Otherwise, only check against other clusters. |
| Fuse Details | |
| Source Distance | Source Distance reference. Whether to consider point bounds, and if so, how. |
| Component Wise Tolerance | If enabled, lets you set individual tolerance in world space for each X, Y and Z axis. |
| Tolerance | Uniform tolerance. This represent the radius within which elements will be considered in fuse range. |
| Tolerances | If enabled, represent individual axis’ radius within which elements will be considered in fuse range. |
| Local Tolerance | If enabled, lets your use per-point tolerance value. NOT IMPLEMENTED |
| Outputs | |
| Snap on Edge | If enabled, snap the intersection position onto the original edge, as opposed to the reverse. |
Intersector Attribute Namebool
| If enabled, flag the points that intersected with an edge. |
Edge/Edge Intersections
Edge/Edge intersections search for Edges that intersect with others Edges. When found, a new Vtx is created at the intersection, creating 4 new edges in place of the previous 2.
| Find Edge Edge Intersections | If enabled, fusing will search for edge/edge intersections. |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Self Intersection | If enabled, a cluster will test if intersection exists against itself. Otherwise, only check against other clusters. |
| Tolerance | |
| Tolerance | Uniform tolerance. This represent the radius within which elements will be considered in fuse range. |
| Min Angle | If enabled, only considers edges to be intersecting if their angle is greater than the specified value. |
| Max Angle | If enabled, only considers edges to be intersecting if their angle is smaller than the specified value. |
| Outputs | |
Crossing Attribute Namebool
| If enabled, flag the edges’ intersection point. |
Blending
See Blending for properties details.
-
Default Points Blendingis used for Point/Point & Point/Edge -
Default Edges Blendingis used for Point/Edge and Edge/Edge - You may use the associated checkbox to override blending settings to get more control over the different processing stages.
Meta Filters
Meta filters lets you choose separately which attributes & tags should carry over from their original data to the new output.
“Carry over” settings lets you pick-and-choose which attributes & tags carry over to the new data.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Preserve Attributes Default Value | If enabled, the node will attempt to create attributes on the data in a way that preserve the original, underlying default value of the attribute. This can be critical in order to identify which data originally belonged to which, as well as properly initializing flags to a desirable default. |
| Attributes | Lets you pick and choose which attributes to keep or dismiss. |
| Tags | Lets you pick and choose which attributes to keep or dismiss. |
Both Attributes & Tags share the same string-based filters.
Note that the filters look for a single valid match amongst the list; you cannot create and/or conditions.
Filter Details
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Filter Mode | Chooses how the filter operates. - All let everything pass.- Exclude filters out the result of the filter.- Include only allows the items that pass the filters. |
| Matches | Lets you define a list of checks pairs: a string value, and a Match Mode. |
| Comma Separated Names | Easy to override, lets you specify a list of comma-separated names. The only caveat is that you can only pick a unique match mode used for each entry. |
| Comma Separated Names Filter | Which filter will be used along the Comma Separated Names. |
| Preserve PCGEx Data | Most of the time you’ll want to leave it to its default value. It ensures PCGEx/ prefixed data are not captured by the filter. |
Filter Modes
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Equals | Checks for strict equality of the filtered value and the associated string. |
| Contains | Checks if the filtered value contains the associated string. |
| Starts With | Checks if the filtered value is prefixed with the associated string. |
| Ends With | Checks if the filtered value is suffixed with the associated string. |