 Pathfinding
Pathfinding
How pathfinding works
Although details vary a bit depending on the selected ⊚ Search algorithm, the basic gist is, for each path & cluster:
- A suitable
SeedandGoalpoint (Vtx) are picked within the cluster. - The Search Algorithm will then find the best path that goes from
SeedtoGoal, accounting for its internal maths, relying on🝰 Heuristics to determine whether one connection is better than another.
- Once a path is found between a given
Seedand itsGoal, traversed points are then added to a dataset, in order fromSeed(start) toGoal(end).
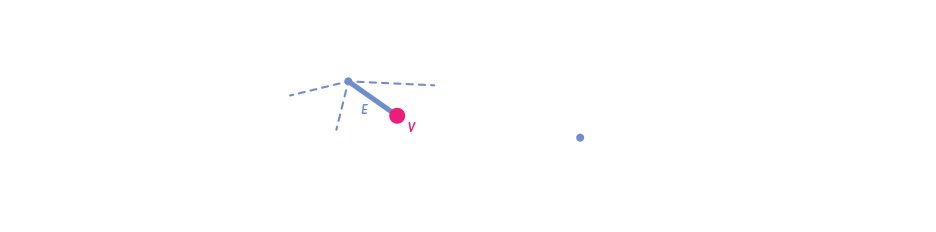
Note: The
SeedandGoalnode are picked based on closest distance to input positions only (point bounds are ignored)
Starting from the seed, each “next step” is weighted according to the V Vertex weight and the E Edge weight that connects to it.
The search returns the path found with the lowest possible weight, or score.
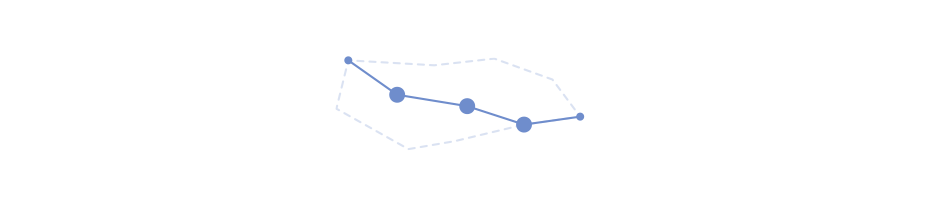
While the selected search algorithm is important, 🝰 Heuristics are more critical to the operation, as user-defined weights can drastically change and shape the path deemed best by the search.
Note: The
Plotnodes variations don’t have a goal picker and instead process each point Dataset as a list of points to go through from start to finish. The first point is the initial seed, the last point is the final goal, and then a path is found that goes through each point in-between, in order.
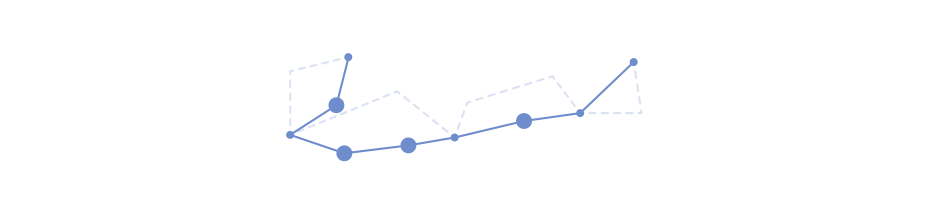
Pathfinding Nodes
Note that there is also two hidden node that enable pathfinding using the existing navmesh:
Navmesh Pathfinding and
Plot Navmesh. They’re not part of the main pool because they’re very legacy. They can still be very useful if you do level blocking with a navmesh, not so much for open world.
Available  🝰 Heuristics modules
🝰 Heuristics modules
🝰 Heuristic Attribute
Attribute-driven heuristics
The Attribute heuristics uses custom point or edge value as raw score.
🝰 Feedback
Favor uncharted points & edges.
The Feedback heuristic add/remove score value to points & edges that are “in use” by other previously computed paths.
🝰 Inertia
Favor active direction preservation.
The Inertia heuristic uses the ongoing traversal data to try and maintain a consistent direction, as if the algorithm had “inertia”.
🝰 Steepness
Favor flat trajectories.
The Steepness heuristic uses the edge angle against an up vector to compute a dot product that is used to determine whether the edge should be considered flat or not.
🝰 Azimuth
Favor edges directed toward the goal.
The Azimuth heuristic attempt to force the path to always aim toward the goal.
🝰 Least Nodes
Favor traversing the least amount of nodes.
The Least Nodes heuristic favor node count traversal over anything else.